Are you eager to learn digital advertising? If so, you should know about the basic advertising terms in order to understand the process of digital advertising. Here, I have listed 100 digital advertising terms. These 100 digital advertising terms are good at the beginner level. Also, I have shared links for most of the terms. By clicking those links you can read more about the terms.
| No | Advertising Term | Explanation |
| 1 | Ad exchange | Ad Exchange is a digital marketplace where publishers and advertisers perform ad inventory trading. Publishers offer their ad space for sale and advertisers buy them if they are interested to show their ads. Example: Google Ad Exchange, OpenX |
| 2 | Ad network | Ad Network is a company that combines the ad inventory from different publishers/websites/apps and sells to the advertiser. Example: Google Adsense, Publift Read Here What is the difference between Ad Network and Ad Exchange? |
| 3 | Ad impression | Impression is the number, how many times an ad is fetched from the ad server and displayed on the user screen. This is a fundamental metric of digital advertising. |
| 4 | Ad server | Ad Server is a platform where advertisers and publishers manage their ads. Ad Servers are responsible to deliver ads to the users and it records performance metrics like impressions and clicks. Example: DCM, Nexd |
| 5 | Ad targeting | Advertisers use various targeting on their ad campaigns to deliver their ads to the right audiences. Example ad targeting: demo targeting, behavior targeting, contextual targeting, device targeting, and so on. |
| 6 | Ad viewability | Ad Viewability is help the advertisers to measure the “seen” impressions. The standard definition indicates that at least 50% of the ad must be in view for at least one second for display ads and two seconds for video ads are considered as “Seen” Impressions. Read More : What is Ad Viewability? Why is Viewability very important for digital ad campaigns? |
| 7 | Affiliate marketing | It’s a type of advertising where anyone can promote the advertiser’s product and get commissions for each sale. They can promote the affiliate products through their websites, blogs, social media and etc. |
| 8 | Behavioral targetings | Based on users’ online behavior and actions like purchases, their interest is determined. Then ads will be targeted based on their interest. So, users are likely to see digital ads related to their interests. |
| 9 | Bid management | Bid Management is the process of optimizing the bid price during ad auctions to achieve a desired goal. It may be a Max CTR, Video Completion Rate, OR Leads. Automated tools and algorithms are used to adjust the bids in real-time. |
| 10 | Brand safety | Brand safety refers to the tools and strategies that ensure an online ad does not appear in a context that could potentially damage the advertiser’s brand & goals. Demand Side Platforms avail this brand safety feature to the marketers. It secures the brand online. Read More : What Is Brand Safety? Importance Of Brand Safety In Digital Advertising |
| 11 | Campaign optimization | Campaign optimization is the process of adjusting the campaign setting in order to maximize the goal. It involves various places like targeting level, bid level, creative level, and etc. Read Here : 6 Common Setup Mistakes That Could Affect Your Ad Campaign Delivery Explained Here |
| 12 | Click-through rate (CTR) | CTR stands for Click Through Rate. CTR means, how many clicks are derived from the impressions. Read More : How To Calculate CTR Of A Digital Campaign? |
| 13 | Conversion rate | Conversion Rate refers to how many users complete the desired action after clicking the ad. A higher conversion rate is good for an ad campaign. |
| 14 | Cost per action (CPA) | CPA is the average amount an advertiser spent for acquiring one desired action, such as sales, leads, form fillings, etc. |
| 15 | Cost per click (CPC) | CPC stands for Cost Per Click. In the CPC model, the advertisers need to pay when users click on their advertisement. This CPC model is mostly used for Search and Display advertising. |
| 16 | Cost per impression (CPM) | CPM means “Cost Per Mille or Cost Per Thousand Impressions”. How much an advertiser needs to pay for 1000 impressions is called CPM. For Example, advertisers kept the CPM as $3 in their campaign means advertisers are willing to pay $3 for 1000 impressions served from the campaign. |
| 17 | Cost per lead (CPL) | Cost per lead (CPL) – The amount an advertiser pays for each lead generated by an ad campaign. CPL is often used in lead generation campaigns, where the goal is to capture contact information from potential customers. |
| 18 | Cost per view (CPV) | Cost per view (CPV) – The amount an advertiser pays each time a video ad is viewed by a user. CPV is often used in video advertising campaigns. |
| 19 | Cross-device targeting | Cross-device targeting is the process of identifying and delivering ads to a particular user across all devices such as Mobile Phones, tablets, Personal computers, and Smart TVs. Cross-Device Targeting is more efficient than other targeting methods. Read More : What Is Cross Device Targeting? How Does Cross Device Targeting Work? |
| 20 | Customer lifetime value (CLV) | Customer lifetime value (CLV) – The estimated value of a customer over the course of their relationship with a business. CLV takes into account factors such as purchase history, average order value, and retention rates to help businesses understand the long-term value of their customers. |
| 21 | Data management platform (DMP) | DMP stands for Data Management Platform which collects, organizes, and activates the data for use in advertising campaigns. Advertisers can use this data and show their ads to the targeted audiences. |
| 22 | Demand-side platform (DSP) | DSP is a Software that has the automatic buying capability to buy advertising spaces for advertisers. DSP supports real-time bidding [Programmatic Bidding]. DSPs are commonly used by advertisers to buy ad inventories in an automatic way. Read More : What is Demand Side Platform? How Does It Work? |
| 23 | Dynamic creative optimization (DCO) | Dynamic creative optimization (DCO) – A technology that allows advertisers to automatically create and serve personalized ad creative based on the user’s location, interests, or other data. DCO can help improve ad engagement and performance by delivering more relevant and personalized ad experiences. |
| 24 | Engagement rate | Engagement Rate is the percentage that tells how much percent of users who have seen your ads interacted with it [like, share, and comment] |
| 25 | Exit rate | The percentage of users who leave a website or digital property after viewing a specific page or set of pages. Exit rate is often used to identify pages or areas of a website that may need optimization to improve user engagement or conversion rates. A lower Exit Rate is good for the website. |
| 26 | Frequency capping | Frequency Capping is the limit, how many times your advertisement shows to the user within a particular duration at maximum. The main purpose of frequency capping is to avoid showing the same advertisement multiple times to the same user. Read More : What Is Frequency Capping? How To Choose Correct Frequency Cap For Your Ad Campaign? Digital Advertising |
| 27 | Geofencing | The practice of using location-based data to create a virtual boundary around a physical location, such as a store or event venue. Geofencing can be used to deliver targeted ads to users within the boundary, or to trigger location-based actions, such as push notifications or discounts. |
| 28 | Geotargeting | Geotargeting is the process of targeting ads to users based on their location. Geotargeting can be based on factors such as zip code, city, state, or country, and can help advertisers reach users in specific markets or regions. |
| 29 | Google AdWords | A platform for creating and managing search engine advertising campaigns on Google’s search results pages and other partner sites. AdWords allows advertisers to bid on specific keywords and target specific audiences and offers a range of ad formats and targeting options to help advertisers reach their goals. |
| 30 | Header bidding | Header Bidding is considered an advanced programmatic advertising technique that works alternative to the waterfall bidding method. It helps publishers to send ad space availability requests to many SSPs or Ad Exchanges simultaneously. Header bidding can help publishers maximize their ad revenue by increasing competition Read More : What Is Header Bidding? Difference Between Waterfall Bidding and Header Bidding? |
| 31 | Hyperlocal advertising | A type of targeted advertising that focuses on reaching users within a specific geographic area, such as a city block or neighborhood. Hyperlocal advertising can be used to promote local businesses or events and is often delivered via mobile devices. |
| 32 | Impression share | The percentage of times an ad is displayed to users compared to the total number of times it could have been displayed. Impression share is often used to measure the effectiveness of ad campaigns and identify areas for improvement. |
| 33 | Influencer marketing | Influencer Marketing is a type of advertising where advertisers partnered with social media influencers and promote their brands to their followers. This is considered to be an effective method to reach young audiences. |
| 34 | In-game advertising | Advertising that appears within video games or mobile games. In-game advertising can take a variety of forms, such as product placements, sponsored levels or features, or display ads. |
| 35 | In-stream advertising | Advertising that appears within a video or audio stream, such as a pre-roll video ad on YouTube or a sponsored segment on a podcast. In-stream advertising can be highly effective because it reaches users who are actively engaged with the content. |
| 36 | Interactive advertising | Advertising allows users to engage with the ad or participate in a related activity, such as playing a game or filling out a survey. Interactive advertising can be highly effective because it encourages user engagement and participation. |
| 37 | Key performance indicator (KPI) | Key performance indicator (KPI) – A measurable metric that is used to evaluate the effectiveness of an ad campaign or marketing effort. KPIs can include metrics such as click-through rate, conversion rate, or revenue generated. |
| 38 | Landing page optimization | It is the process of improving the user experience on the landing page after they landed on the landing page by clicking the ad. By improving the landing page optimization, you can increase the conversion rate. |
| 39 | Lookalike targeting | It’s a type of targeting that identifies users who have similar characteristics or behaviors to a particular audience or customer segment. Lookalike targeting can help advertisers reach new users who are likely to be interested in their products or services. |
| 40 | Native advertising | Advertising that is designed to blend in with the surrounding content, such as sponsored posts on social media or sponsored articles on news websites. Native advertising can be highly effective because it is less intrusive than traditional display ads. |
| 41 | OOH Advertising | OOH advertising means “Out Of Home” Advertising. If you are seeing any visual advertisements outside of your home called OOH advertising. For example, Flex Boards or Billboards, Signs, ads on buses or trains, travel stations, cinema stations, malls, etc. Read More : What Are OOH, DOOH, pDOOH Advertising? How Do They Work? |
| 42 | Paid search | Advertising that appears at the top of search engine results pages, based on keywords or search queries. Paid search can be highly effective because it reaches users who are actively searching for products or services. |
| 43 | Pay-per-click (PPC) | Pay-per-click (PPC) – A pricing model for digital advertising in which advertisers pay each time a user clicks on their ad. PPC can be highly effective because it allows advertisers to only pay for the clicks they receive. |
| 44 | Programmatic advertising | Software or Program used to buy and sell digital ad space is called as “Programmatic Advertising”. Rather than buying and selling the ad space, it helps to do targetings, and optimizations to the digital campaigns. Read More: What is Programmatic Advertising? How Does It Work? |
| 45 | Reach | Reach: Reach refers to the number of people who see or are exposed to an advertisement. It is a key metric for measuring the effectiveness of advertising campaigns. |
| 46 | Real-time bidding (RTB) | Real Time Bidding is an instant auction for buying and selling ad inventories in real time. Real Time Bidding is facilitated by Ad Exchanges or Supply Side Plarform. Read More : What Is Real Time Bidding? How Does Real Time Bidding Work? |
| 47 | Remarketing | Remarketing or Retargeting is a concept that allows advertisers to show an advertisement to the user who already visited the advertiser’s site or users who have already interacted with the advertiser’s site. |
| 48 | Retargeting | Retargeting is similar to remarketing, but it specifically targets users who have shown interest in a specific product or service, by showing them relevant ads as they browse other websites or social media platforms. |
| 49 | Rich media | Rich Media refers to ads that contain interactive content like video, audio, animation etc. |
| 50 | Search engine optimization (SEO) | SEO is the practice of optimizing a website to improve its visibility and ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs) with the aim of driving organic traffic. |
| 51 | Search engine marketing (SEM) | SEM is a form of digital advertising that involves placing ads on search engine results pages (SERPs) with the aim of driving traffic to a website or landing page. |
| 52 | Site retargeting | Site retargeting is the process of identifying the best performing sites and showing ads on the websites without considering the user interest. So, whoever visits the site will see your ads. |
| 53 | Social media advertising | Social media advertising involves placing ads on social media platforms with the aim of reaching and engaging with a target audience. |
| 54 | Sponsored content | Sponsored content is content that is created by an advertiser and published on a third-party platform with the aim of promoting a product or service. |
| 55 | Supply-side platform (SSP) | SSP is software, publishers use this software to manage & sell their ad inventory in an automatic way. By using SSP, publisher can serve display, video, native ads on their websites, Apps”. Demand Side Platforms available to help the advertisers and Server Side Platforms are available to help the publishers. Like DSP, SSP also has many features that would be helpful for the publishers. By managing their campaign in SSP, they can block any particular ad or advertisers or control the frequency or bid rate and more. Read More : What is Supply Side Platform (SSP)? How Does It Work? |
| 56 | Target audience | The target audience is the specific group of people that an advertiser is trying to reach and engage with through their advertising campaigns. |
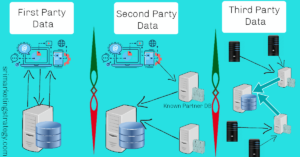
| 57 | Zero Party Data | First Party Data is the data, companies collect from its own resources. But, Zero Party Data means the data users intentionally shared with companies. Users intentionally shared their interest, personal information — name, email id, phone number with companies to enjoy some benefits provided by the company. For example, Provide email id to download the free course document, newsletter signups, customer surveys, etc. Read More : What Are Zero Party Data, First Party Data, Second Party Data, and Third Party Data? |
| 58 | Tracking pixel | A tracking pixel is a small, transparent image embedded in a web page or email that allows advertisers to track user behavior and measure the effectiveness of their advertising campaigns. Read More : What Is Tracking Pixel In Digital Advertising? How Does It Work? Advantages and Disadvantages Of Tracking Pixels? |
| 59 | Unique visitor | A unique visitor refers to a single individual user who visits a website or interacts with an advertisement within a given time period, regardless of how many times they visit or interact. |
| 60 | User-generated content (UGC) | UGC refers to content such as photos, videos, and comments that are created by users of a website or social media platform. Advertisers can leverage UGC to engage with their target audience and promote their brand. |
| 61 | Viewability rate | Viewability rate is a metric used to measure the percentage of ad impressions that are actually viewable by users. |
| 62 | View-through rate (VTR) | VTR is a metric used to measure the percentage of users who view an ad and then go on to take a desired action, such as visiting a website or making a purchase. |
| 63 | Viral marketing | Viral marketing is a marketing technique that involves creating content that is designed to be shared rapidly and widely by users, with the aim of increasing brand awareness and engagement. |
| 64 | Web analytics | Web analytics refers to the collection, measurement, and analysis of data related to website traffic and user behavior. This data is used to optimize website performance and improve the effectiveness of advertising campaigns. |
| 65 | Above the fold | Above the fold refers to the portion of a web page that is visible without scrolling down. Advertisers often aim to place their ads above the fold in order to increase visibility and engagement. |
| 66 | Ad copy | Ad copy refers to the text or language used in an advertisement. Effective ad copy is crucial for capturing the attention of the target audience and encouraging engagement. |
| 67 | Ad placement | Ad placement refers to the location on a web page or within an app where an advertisement is displayed. The placement of an ad can have a significant impact on its visibility and effectiveness. |
| 68 | Advertiser | An advertiser is a company or individual that creates and places advertisements in order to promote their products or services. |
| 69 | Attribution window | An attribution window is a specific time period during which an advertiser can attribute a desired action, such as a purchase or website visit, to a specific advertising campaign. |
| 70 | Blacklist | A blacklist is a list of websites or apps that an advertiser has excluded from their advertising campaigns due to concerns around content, audience demographics, or brand safety. |
| 71 | Bot traffic | Bot traffic refers to non-human traffic that visits a website or interacts with an advertisement. This type of traffic can be generated by bots or automated software programs and can skew advertising metrics. |
| 72 | Branding campaign | A branding campaign is an advertising campaign that is designed to increase brand awareness and visibility, rather than drive immediate sales or conversions. |
| 73 | Budget pacing | Budget pacing is the process of managing advertising spend in order to ensure that a campaign stays within its allocated budget. Example : Daily, Even Through Period, Lifetime, ASAP |
| 74 | Call-to-action (CTA) | A call-to-action is a prompt or instruction that encourages users to take a specific action, such as clicking a button or making a purchase. CTAs are often used in advertising to encourage engagement and drive conversions. |
| 75 | Carousel ad | A carousel ad is a type of advertising format that allows users to swipe or scroll through multiple images or videos within a single ad unit. |
| 76 | Chatbot | A chatbot is an automated software program that interacts with users via messaging platforms or chat windows. Chatbots can be used for a variety of purposes, including customer service, lead generation, and advertising. |
| 77 | Click fraud | Click fraud refers to the practice of clicking on ads with the intention of generating revenue or artificially inflating ad metrics. |
| 78 | Contextual targeting | Contextual targeting is a type of advertising targeting that uses contextual cues, such as the content of a web page or the keywords in a search query, to deliver relevant ads to users. Read More : What Is Contextual Targeting? How It Works? Benefits? |
| 79 | Conversion funnel | A conversion funnel is a visual representation of the steps that users take to complete a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form. Advertising campaigns are often designed to drive users through the conversion funnel. |
| 80 | Conversion pixel | A conversion pixel is a small piece of code that is placed on a website or landing page and used to track user behavior and measure the effectiveness of advertising campaigns. |
| 81 | Cost per completed view (CPCV) | CPCV is a metric used to measure the cost of each view of an ad that is played to completion. |
| 82 | Cost per install (CPI) | CPI is a metric used to measure the cost of each new app installation resulting from an advertising campaign. |
| 83 | Creative testing | Creative testing is the process of testing different versions of ad creative, such as images, videos, or headlines, in order to determine which performs best. Conducting creative tests before live is a good practice. |
| 84 | Custom audience | A custom audience is a group of users who have interacted with a brand or website in a specific way, such as making a purchase or visiting a particular page. Custom audiences can be used for targeted advertising campaigns. |
| 85 | Direct response advertising | Direct response advertising is a type of advertising that is designed to elicit an immediate response from the viewer or listener, such as making a purchase or filling out a form. |
| 86 | Display advertising | Display advertising is a type of online advertising that includes banner ads, pop-up ads, and other visual ads that are displayed on websites and apps. |
| 87 | DMA (Designated Market Area) | A DMA is a geographic area that is used by advertisers to target specific regions or markets for advertising campaigns. |
| 88 | Email marketing | Email marketing is a type of direct marketing that involves sending promotional messages and offers to a list of email subscribers. |
| 89 | Frequency | Frequency refers to the number of times an ad is shown to a particular user or audience within a given time period. |
| 90 | Geo-farming | Geo-farming is a type of mobile advertising that targets users based on their geographic location, typically using GPS or other location data. |
| 91 | Google Analytics | Google Analytics is a web analytics tool that provides insights and data on website traffic, user behavior, and other metrics. |
| 92 | In-banner video | In-banner video is a type of display advertising that includes video content within a banner ad. |
| 93 | Incentivized traffic | Incentivized traffic refers to traffic that is generated through the use of incentives, such as rewards or discounts, for taking a specific action, such as clicking on an ad. |
| 94 | Lookback window | A lookback window is a timeframe used to track user behavior and attribute conversions to specific advertising campaigns or channels. |
| 95 | Podcast advertising | Podcast advertising: Podcast advertising is a type of advertising where ads are inserted into podcasts or other audio content. |
| 96 | Pre-roll ad | Pre-roll ad: A pre-roll ad is a type of video ad that is played before a user’s selected video content. |
| 97 | Private marketplace (PMP) | Private marketplace (PMP): A private marketplace is a type of programmatic advertising where publishers offer premium inventory to a select group of advertisers. |
| 98 | Programmatic direct | Programmatic direct: Programmatic direct is a type of programmatic advertising where advertisers buy inventory directly from publishers, rather than through an ad exchange or other intermediary. |
| 99 | Quality score | Quality score is a metric used in search engine advertising that measures the quality and relevance of ads and landing pages. |
| 100 | Return on ad spend (ROAS) | Return on ad spend (ROAS): ROAS is a metric used to measure the revenue generated by advertising campaigns compared to the cost of the advertising. |
| 101 | Return on investment (ROI) | ROI is a metric used to measure the profitability of advertising campaigns, calculated as the revenue generated by the campaign divided by the cost of the campaign. |
| 102 | Win rate | Win rate is a metric used in programmatic advertising to measure the percentage of bids that are successful in winning an auction for ad inventory. |
| 103 | Ad fraud | Ad fraud refers to fraudulent activities in advertising, such as click fraud, where fake clicks are generated to increase ad revenue. |
| 104 | Ad verification | Ad verification is the process of ensuring that an ad is displayed in a safe and brand-appropriate environment, often through the use of third-party verification tools. Read More : What is Ad Verification? How does it work? Top ad verification vendors list |
| 105 | DOOH Advertising | DOOH advertising means – visual advertising shown on digital screens which are placed out of home, such as Mall Entrance, Theaters, Road Side Walls, Building Walls, Airport, etc. Still, most marketers have a good interest in OOH advertising due to its advantage. Now the availability of technology and low-cost digital screens gives the opportunity to grow DOOH advertising. Read More : What Are OOH, DOOH, pDOOH Advertising? How Do They Work? |
| 106 | pDOOH Advertising | Programmatic DOOH is a process of selling and buying ad space in an automated way. Ad Space [Digital Screen] is open for all bidders and those who bid the most will get the opportunity to show their ad – real time bidding. |
| 107 | First Party Data | First Party Data is the data that companies collect from their own resources like own Websites, Applications or Social Media Pages and Offline Sources. Big marketers interested to collect first party data because it is more valuable than third party data. |
| 108 | Second Party Data | Information collected from your trusted partner and shared with your company is called as Second Party Data. Second Party data is another company’s first party data. You know very well about this partner company and they share their first party data with you for money or any other benefit. So, this information is accurate and helpful to expand your audience size. |
| 109 | Third Party Data | Third Party Data is the data collected by the outside sources and they do not have any direct relationship with the customers (they are not the original collectors of that data). Those outside data providers collect the data from various websites, platforms, and applications. If any advertiser needs to show their advertisements to any particular group of audiences then they can purchase the data through the demand side platform. Read More : What Are Zero Party Data, First Party Data, Second Party Data, and Third Party Data? |
Conclusion :
I hope, I covered most of the digital advertising terms here. Also, added additional links to most of the terms. If you are going to attend a job interview in the digital advertising domain then read about all the common digital advertising terms. I will add new terms periodically. Thank You!